This functionality controls user access to specific software programs, governed using a combination of iLab’s Scheduling and Calendars functionality, Equipment Kiosk interface, and Sassafras K2-KeyServer.
Once you have received the required devices, software and completed set up and implementation, refer to Setting Up Software Interlock.
Sassafras KeyServer
Sassafras KeyServer (formerly known as K2-KeyServer) is an IT asset management tool that tracks both hardware and software usage across an institution. It can discover installed software, monitor who is using it and how often, and generate detailed usage reports.
When integrated with iLab, KeyServer can enforce software usage policies by consulting the iLab database. This allows software access to be restricted based on training status or instrument scheduling, ensuring only authorized users can launch controlled applications.
A unique Sassafras KeyServer (the core server component of the AllSight platform) needs to be installed within the institution's network. This KeyServer is responsible for managing any computers that will use the Software Interlock functionality.
If an institution already has an existing installation of Sassafras KeyServer (used for general license tracking or other asset management), we recommend configuring a separate, dedicated instance to avoid potential conflicts with Deny/Control policies or version upgrade dependencies.
iLab recommends that the institution assign a central point of contact (POC) to work with both iLab and Sassafras during the installation and configuration of the Software Interlock KeyServer. Ideally, this POC should come from the institution’s IT department, as they will be responsible for ongoing support and management.
Each computer that hosts controlled software must have the Sassafras KeyAccess client installed. KeyAccess allows the KeyServer to recognize the machine, gather inventory data, and apply software usage policies.
Institutions and/or core facilities must purchase enough KeyAccess licenses to cover the total number of computers that will run controlled software—not the total number of software applications.
Please provide local administrative access to the Sassafras KeyConfigure interface. KeyConfigure is the graphical administration console used to manage client computers, view installed software, and configure Control and Deny policies for software usage.
Any computer on the institution’s network that needs to use the Software Interlock solution must have network connectivity to the KeyServer. Internet access is not required, but these machines must be able to communicate with the KeyServer on the local network to enforce software usage restrictions.
Additional information on how to set up Sassafras for use with iLab can be found using the iLab/Sassafras Documentation and Sassafras iLab Integration Article
On-site Requirements
Personnel Requirements
Coordination will be required with the institution’s IT and networking teams. The IT professionals should be able to follow the instructions below and utilize the linked resources in this document to set up the bridge.
Network Requirements
An onsite IT team will need to create a secure local network in which the iLab Bridge will reside. The Bridge and Sassafras server do not have to be on the same subnet:
- The Bridge needs only to be able to connect to the internet.
- When the Bridge is installed, the Sassafras server should be able to connect to the Bridge on port 3306 to send MySQL requests.
iLab Bridge
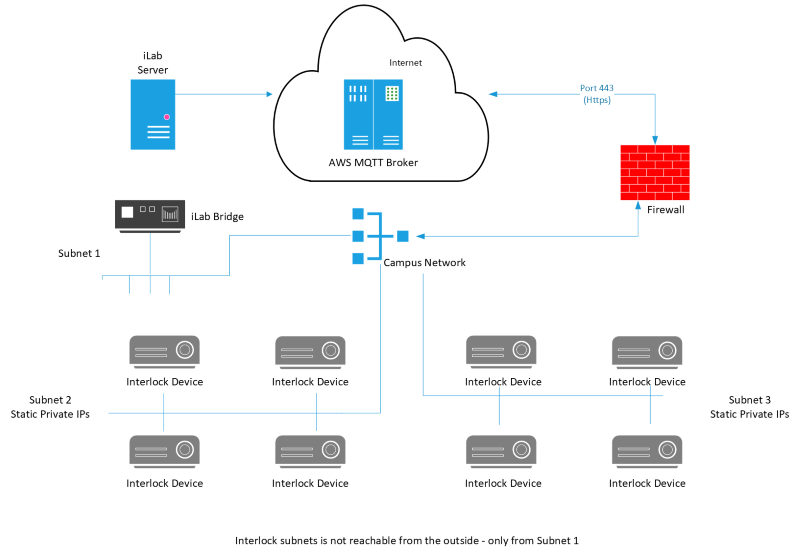
Once an agreement is in place, the iLab engineering team will configure and send you an iLab bridge. Your interlock devices will be connected to this bridge, which will require a static IP. The bridge will establish a secure HTTPS (Port 443) connection to AWS (Amazon Web Services) IoT services from within your organization. The bridge and the subnet do not need to be exposed to the outside world; only the bridge needs to have internet connectivity.
There are two possible scenarios for how your devices will connect to the VLAN/subnet:
- Multiple devices on one subnet
- Multiple devices on multiple subnets
Diagram 1: Multiple devices on one subnet
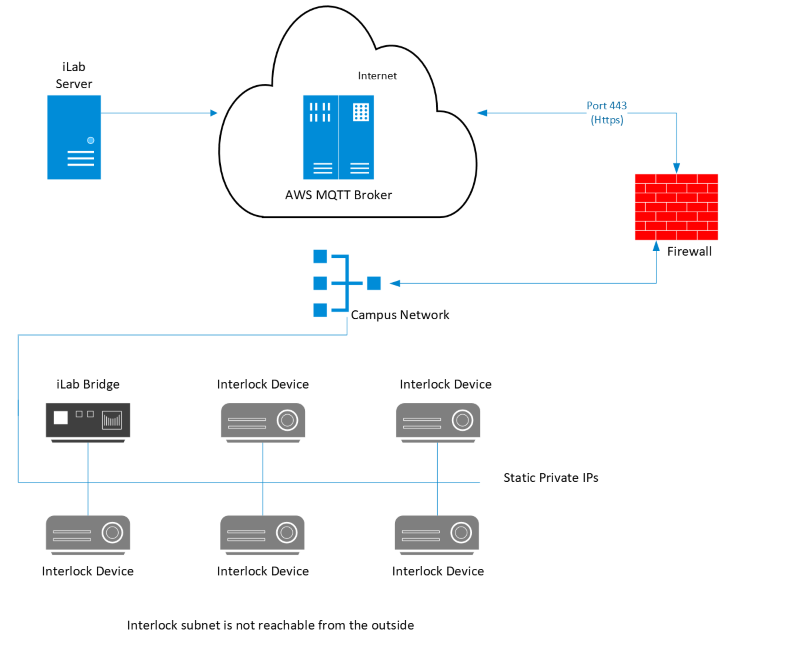
Diagram 2: Multiple devices on multiple subnets